Pressable uses React Native's Pressability API. For
more information around the state machine flow of Pressability and how it
works, check out the implementation for
Pressable uses React Native's Pressability API. For
more information around the state machine flow of Pressability and how it
works, check out the implementation for
refreshing is a controlled prop, which is why it needs to
be set to true in the onRefresh function otherwise the refresh
indicator will stop immediately.
SafeAreaView will be ignored and can cause
different results depending on the platform. See{' '}
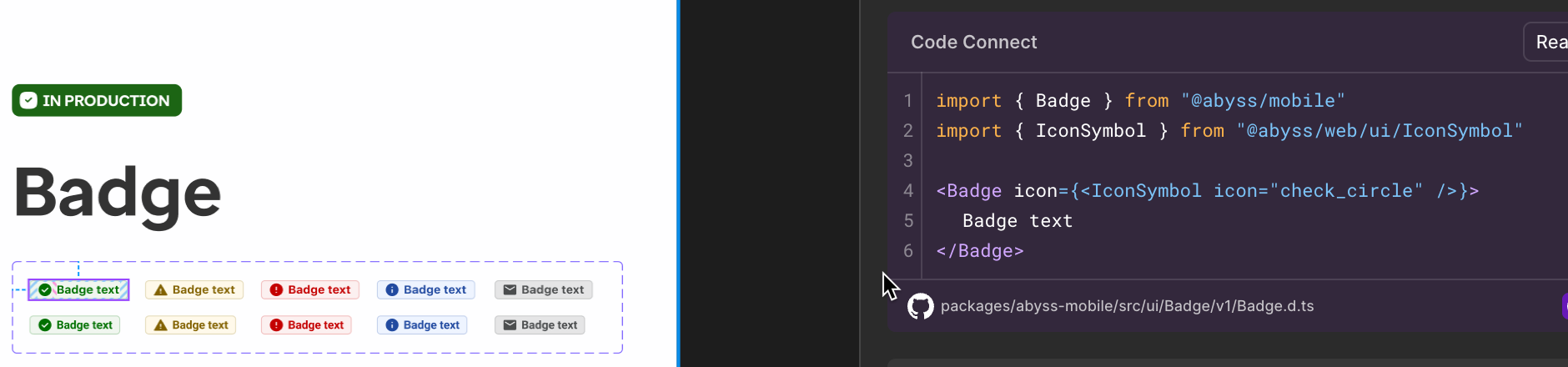 ```
#### Slot limitations
At this time, code connect does not support slots. If you need to use a slot, you will need to manually add it to the code after copying it from Code Connect.
The reccomended code section does not show the actual slot element's code.
```jsx render
```
#### Slot limitations
At this time, code connect does not support slots. If you need to use a slot, you will need to manually add it to the code after copying it from Code Connect.
The reccomended code section does not show the actual slot element's code.
```jsx render
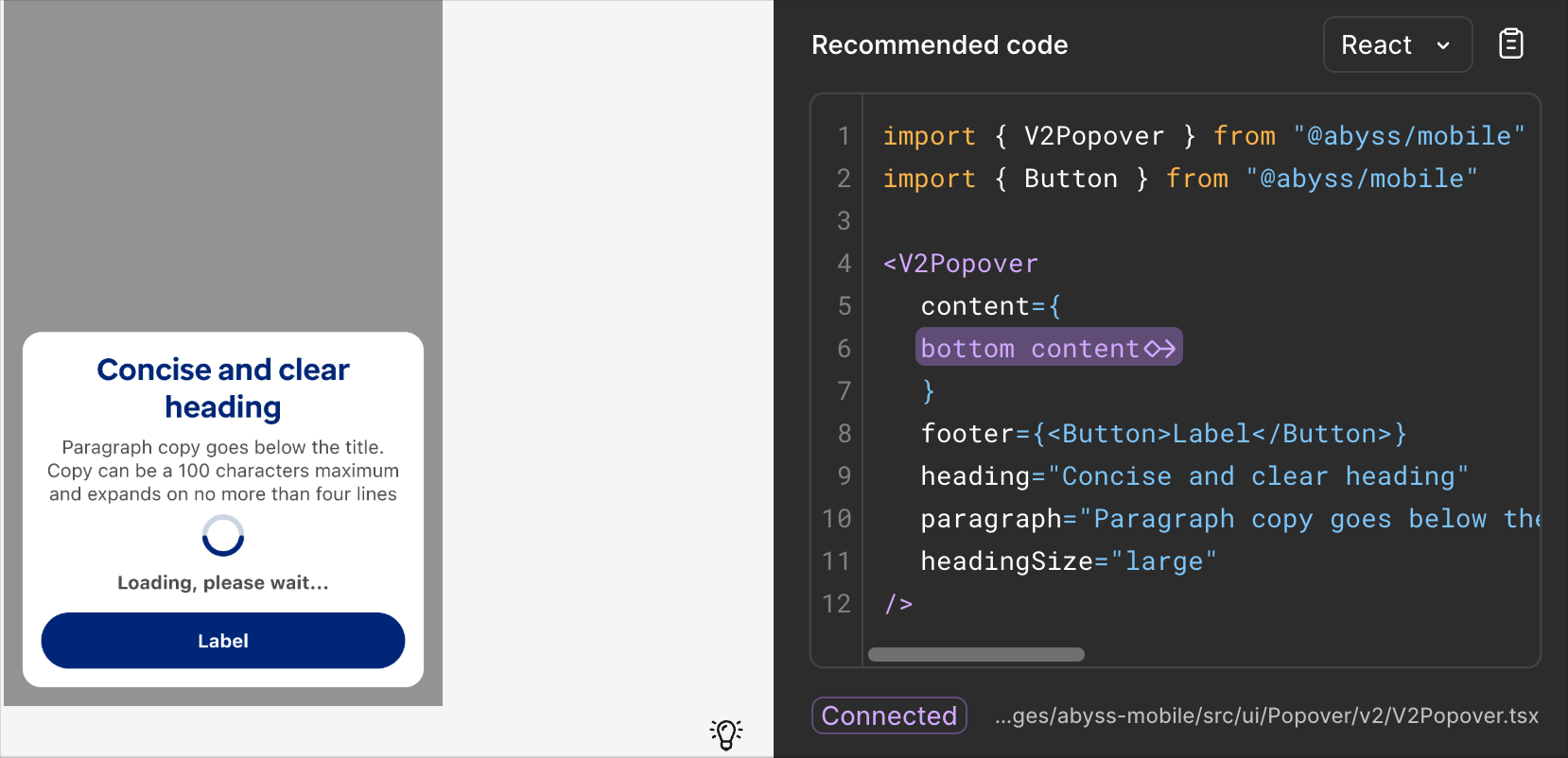 ```
### Supported Components
```jsx render
```
### Supported Components
```jsx render

Single Value: {JSON.stringify(singleValue)}
Multiple Values: {JSON.stringify(multipleValues)}
All Values: {JSON.stringify(allValues)}
 ---
id: use-style-sheet
category: Styling
title: useStyleSheet
description: Used to parse styles from a StyleSheet
---
```jsx
import { useStyleSheet } from '@uhg-abyss/mobile';
```
The `useStyleSheet` hook helps to parse the additional functionality from the Abyss [StyleSheet](/mobile/ui/style-sheet).
## Usage
```tsx
useStyleSheet(styles: object): object
```
Take a look at StyleSheet below:
```jsx
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
padding: '$xs * 4px',
margin: '$fontScale',
},
label: {
color: '$gray4',
fontWeight: '$bold',
fontSize: '$lg',
marginVertical: '$md * 2',
fontFamily: '$heading',
},
box: {
backgroundColor: '$interactive1',
borderColor: '$error1',
borderRadius: '$md * $sm',
borderWidth: 4,
width: '6rem',
height: '48px * 3',
marginBottom: '32px - 0.75rem',
'@media (min-width: 767px)': {
width: '12rem',
},
},
});
```
There's a lot of code that is unfamiliar to the normal StyleSheet. Above, there are _**media queries**_,
_**tokens**_, _**operations**_, _**rem values**_, and _**pixel values**_, which normally would not be able to be parsed by React
Native core component. This is where the `useStyleSheet` hook comes in. By using the hook, we can parse these
value into value that the core component can understand.
```jsx live
const themedStyles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
padding: '$xs * 4px',
margin: '$fontScale',
},
label: {
color: '$gray4',
fontWeight: '$bold',
fontSize: '$lg',
marginVertical: '$md * 2',
fontFamily: '$heading',
},
box: {
backgroundColor: '$interactive1',
borderColor: '$error1',
borderRadius: '$md * $sm',
borderWidth: 4,
width: '6rem',
height: '48px * 3',
marginBottom: '32px - 0.75rem',
'@media (min-width: 767px)': {
width: '12rem',
},
},
});
render(() => {
const styles = useStyleSheet(themedStyles);
return (
---
id: use-style-sheet
category: Styling
title: useStyleSheet
description: Used to parse styles from a StyleSheet
---
```jsx
import { useStyleSheet } from '@uhg-abyss/mobile';
```
The `useStyleSheet` hook helps to parse the additional functionality from the Abyss [StyleSheet](/mobile/ui/style-sheet).
## Usage
```tsx
useStyleSheet(styles: object): object
```
Take a look at StyleSheet below:
```jsx
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
padding: '$xs * 4px',
margin: '$fontScale',
},
label: {
color: '$gray4',
fontWeight: '$bold',
fontSize: '$lg',
marginVertical: '$md * 2',
fontFamily: '$heading',
},
box: {
backgroundColor: '$interactive1',
borderColor: '$error1',
borderRadius: '$md * $sm',
borderWidth: 4,
width: '6rem',
height: '48px * 3',
marginBottom: '32px - 0.75rem',
'@media (min-width: 767px)': {
width: '12rem',
},
},
});
```
There's a lot of code that is unfamiliar to the normal StyleSheet. Above, there are _**media queries**_,
_**tokens**_, _**operations**_, _**rem values**_, and _**pixel values**_, which normally would not be able to be parsed by React
Native core component. This is where the `useStyleSheet` hook comes in. By using the hook, we can parse these
value into value that the core component can understand.
```jsx live
const themedStyles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
padding: '$xs * 4px',
margin: '$fontScale',
},
label: {
color: '$gray4',
fontWeight: '$bold',
fontSize: '$lg',
marginVertical: '$md * 2',
fontFamily: '$heading',
},
box: {
backgroundColor: '$interactive1',
borderColor: '$error1',
borderRadius: '$md * $sm',
borderWidth: 4,
width: '6rem',
height: '48px * 3',
marginBottom: '32px - 0.75rem',
'@media (min-width: 767px)': {
width: '12rem',
},
},
});
render(() => {
const styles = useStyleSheet(themedStyles);
return (
| Scale | Percent |
|---|---|
| XL | 110% |
| XXL | 120% |
| XXXL | 130% |
| AX1 | 179% |
| AX2 | 214% |
| AX3 | 264% |
| AX4 | 314% |
| AX5 | 357% |
 }
footer={
}
>
In this example the header has no padding or margin on the top and
sides, and reduced margin on the bottom. This allows for full fill
images.
}
footer={
}
>
In this example the header has no padding or margin on the top and
sides, and reduced margin on the bottom. This allows for full fill
images.
 ## Subtitles/CC
Be sure to add closed captions to your video via the `textTrack` prop.
Closed Captions are required for accessibility. You can provide multiple text tracks, and select the default one using the `selectedTextTrack` prop.
```jsx
## Subtitles/CC
Be sure to add closed captions to your video via the `textTrack` prop.
Closed Captions are required for accessibility. You can provide multiple text tracks, and select the default one using the `selectedTextTrack` prop.
```jsx